Mainstream gaming on Linux has been steadily improving year after year, with better compatibility, performance, and a growing library of supported titles, making it a viable alternative to Windows and console gaming.
In contrast, the emulation scene has been around for much longer within the Linux community, thriving thanks to Linux's openness and DIYbility. There are even dedicated retro gaming distros like Lakka and RetroPie that make setting up and playing classic games on Linux easy.
In this article, we'll be taking a look at RetroArch, a popular emulation frontend available for Linux and many other platforms.
RetroArch: Overview ⭐
Before you think that RetroArch is an emulator, don't. It's actually a frontend that runs emulators through a system of modular components called Libretro cores. Each core handles a specific console or platform, allowing RetroArch to support a wide range of classic systems.
It’s also more than just a game launcher. RetroArch can run media players, game engine ports, and offers features like game rewinding, shaders, and multiplayer support.
⭐ Key Features
Packing a wide range of features that complement gameplay, customization, and compatibility across platforms, RetroArch has the following standout features:
**Cross-platform.****Supports over 200 cores.****Unified settings interface.**Can run media from discs.
🎮 Gaming Experience
On my Bazzite setup, I installed the RetroArch Flatpak and connected an Xbox Wireless controller to try out Freedoom, a free game that plays like classic DOOM. Using the PrBoom core, it ran smoothly without any major issues.
Initially, I had tried using the Steam version of RetroArch, but it was a bit tricky to manually add cores and games since that version doesn’t have the online downloader.
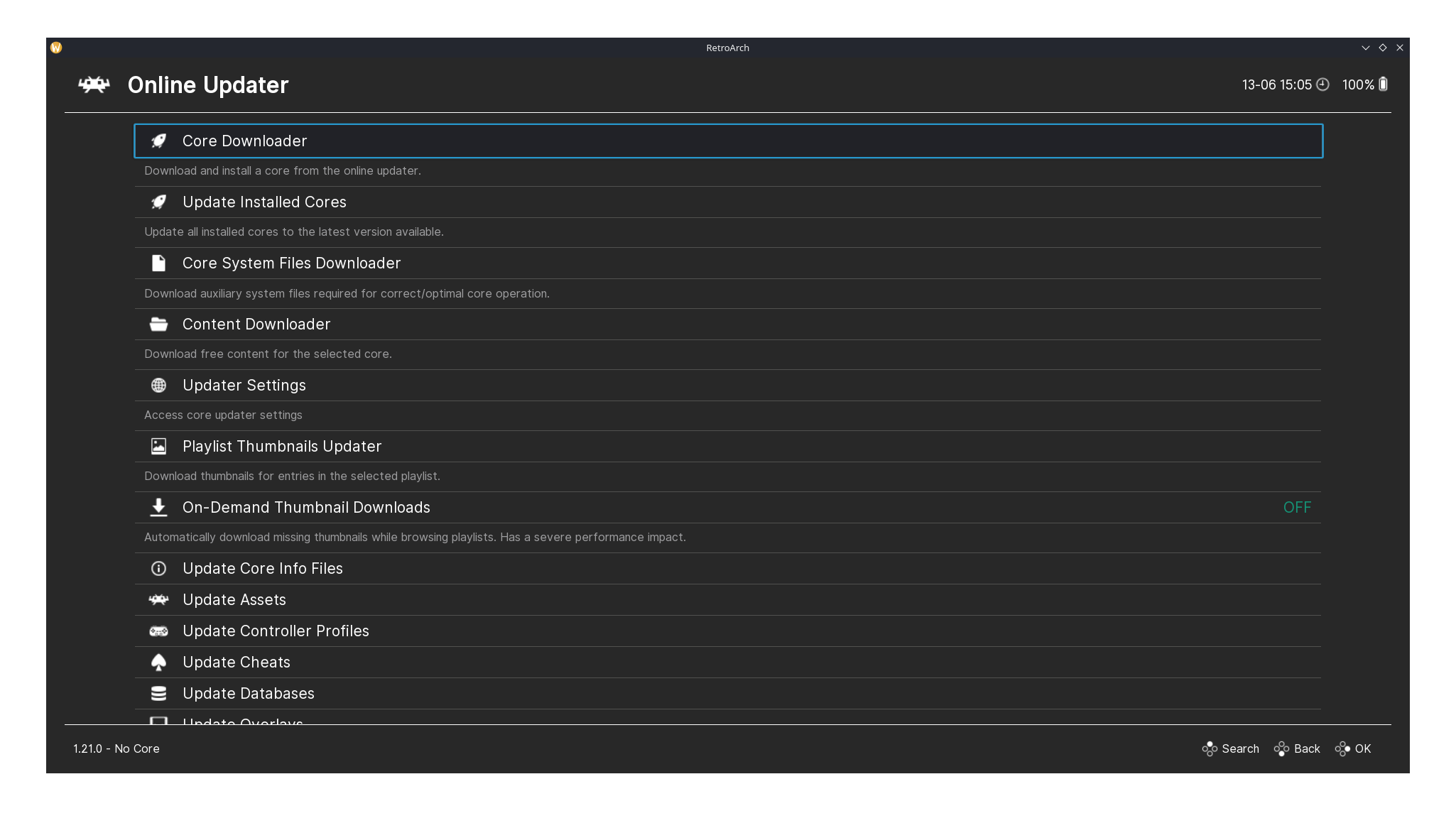
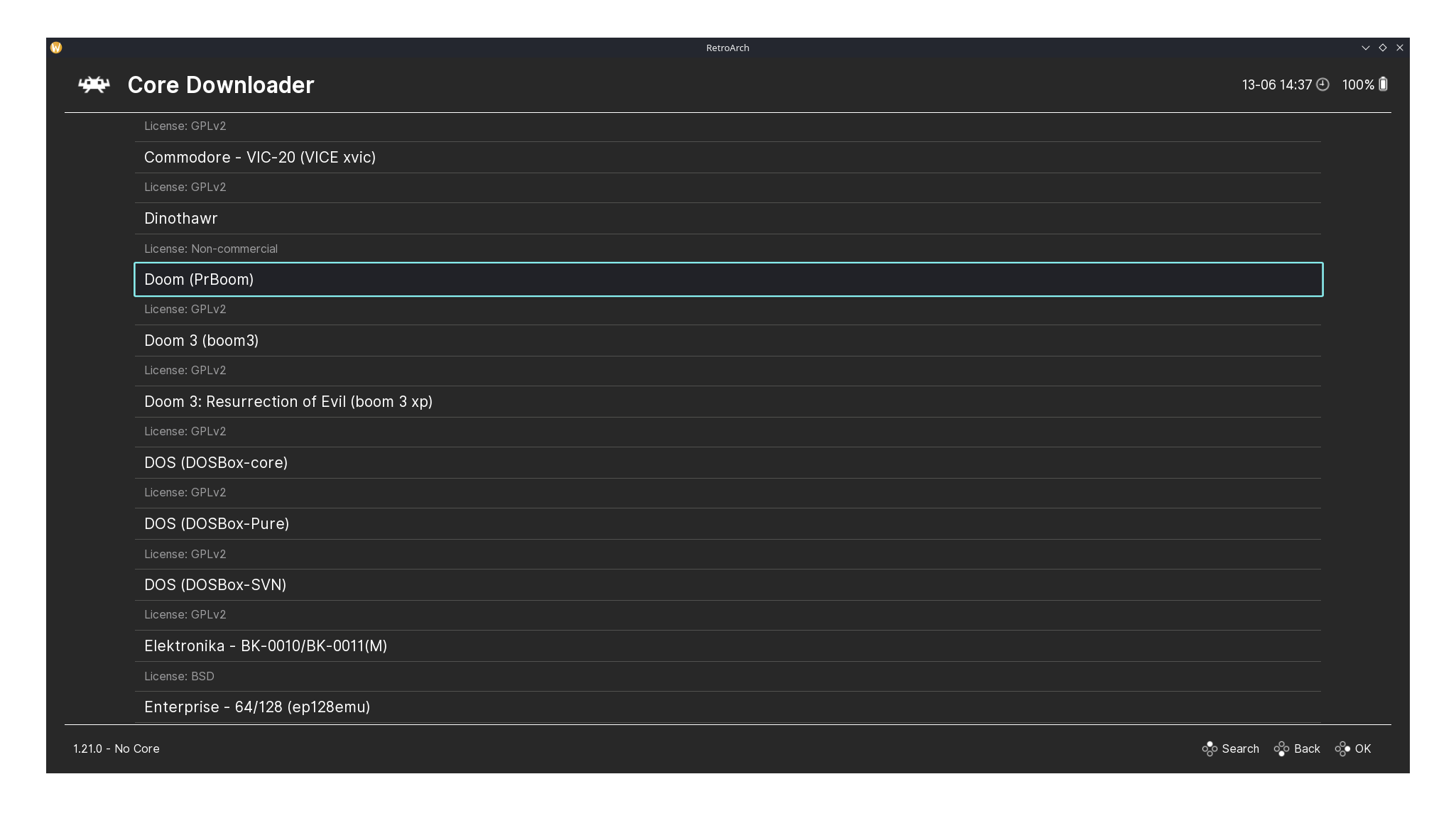
The Online Updater and Core Downloader pages of RetroArch.
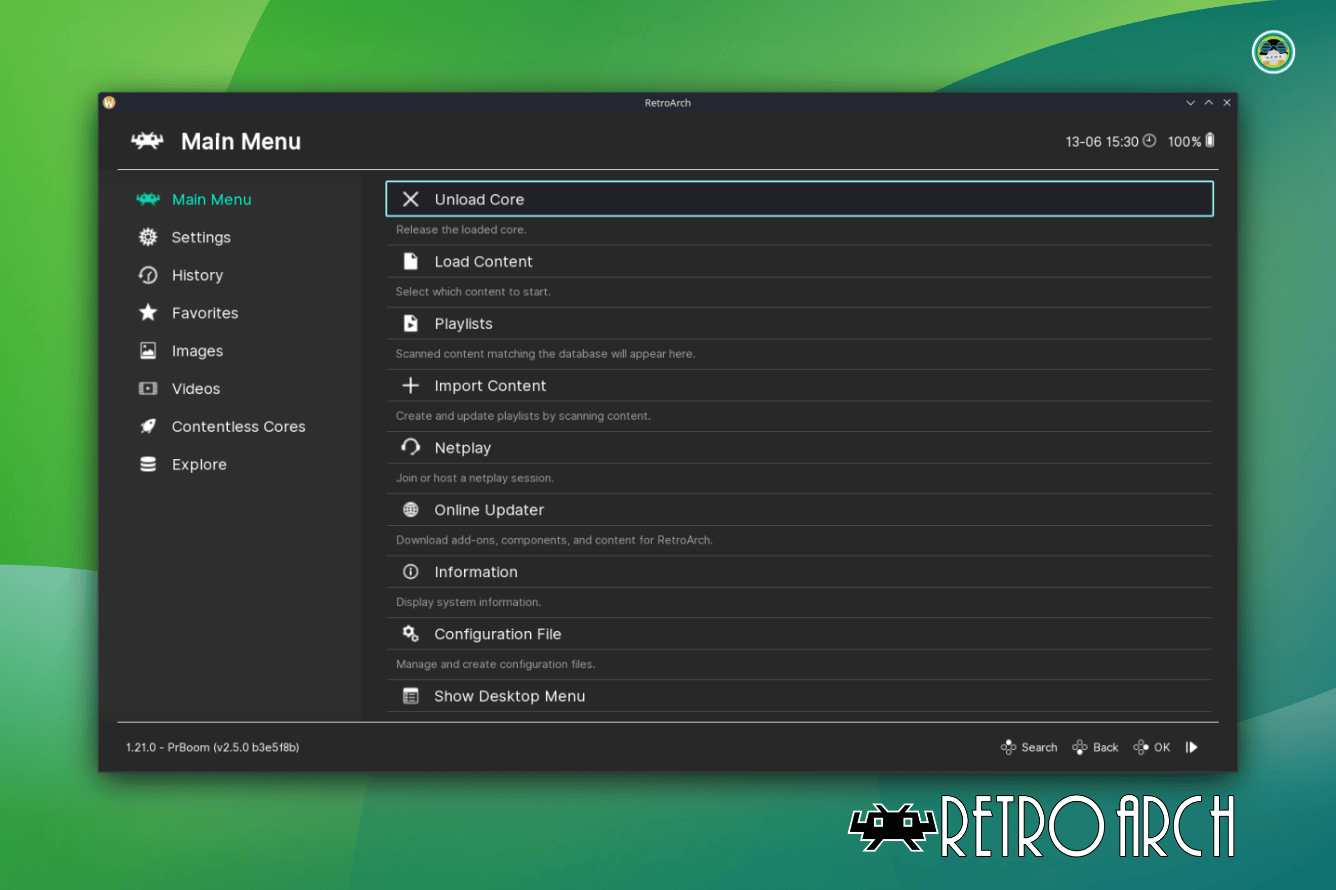
I downloaded the PrBoom core using RetroArch’s built-in Online Updater, which offers many cores for playing games from various classic consoles and systems. Using my controller, I easily navigated to the Core Downloader page from the Main Menu to find the core.
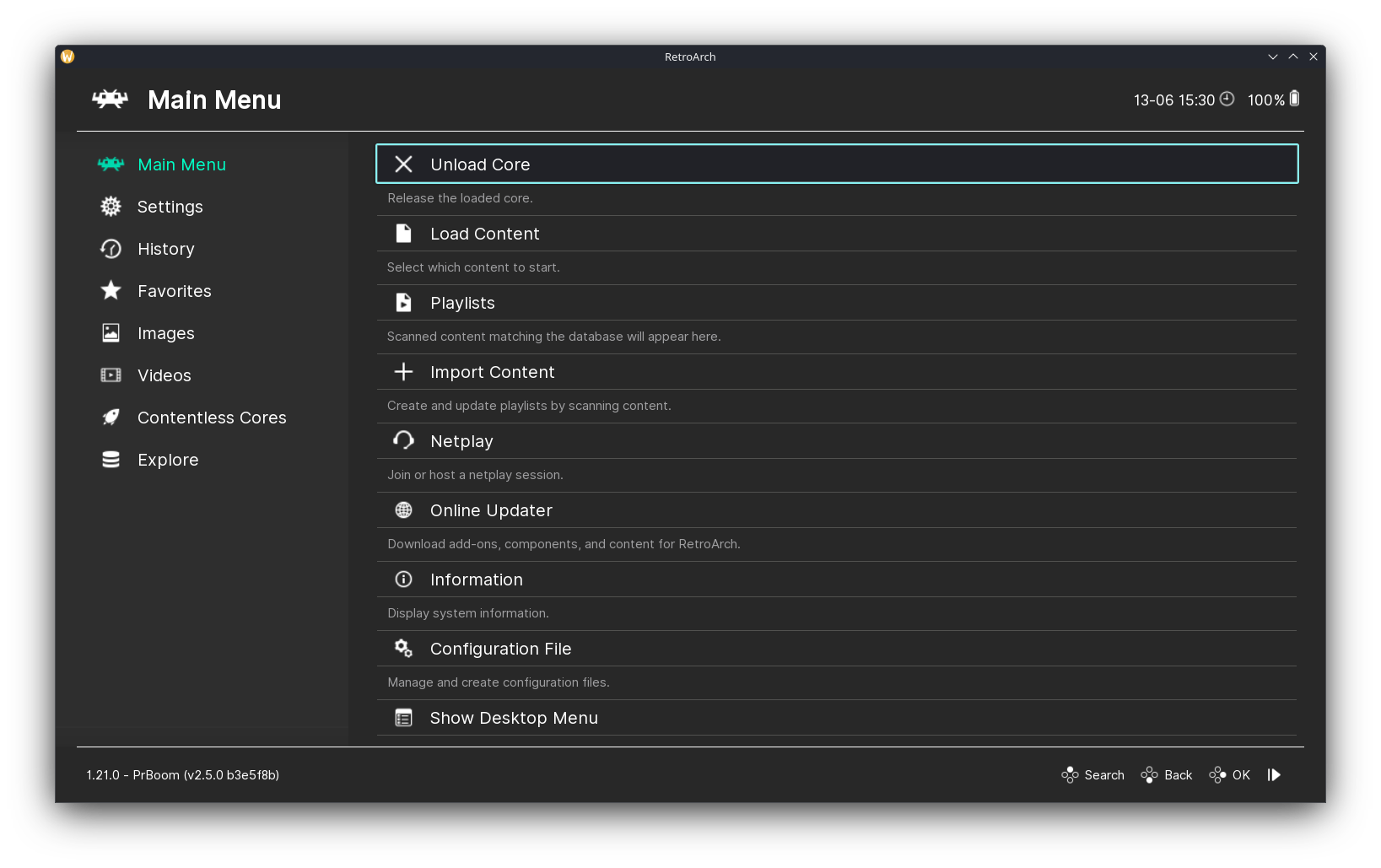
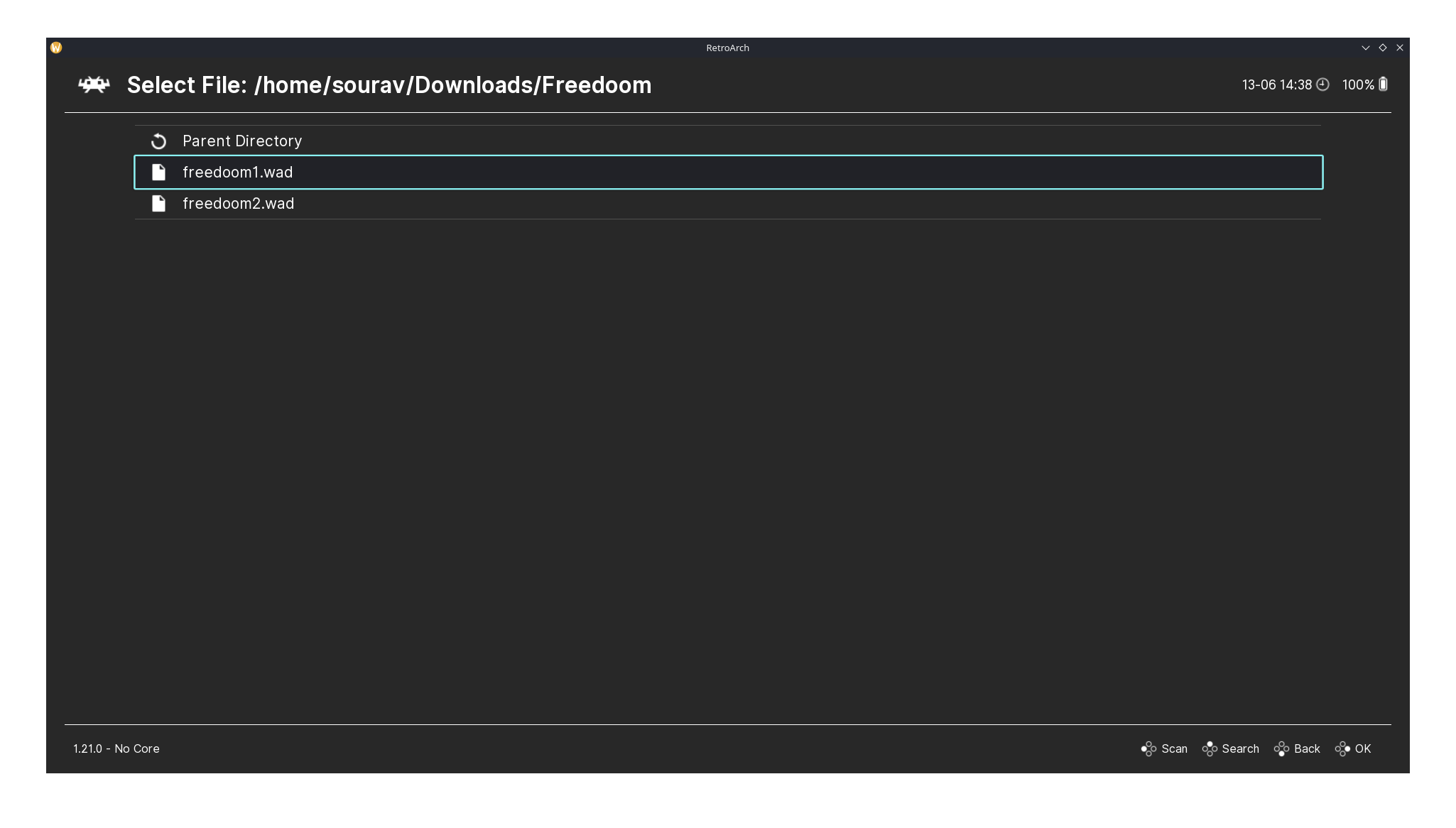
The Main Menu and Load Content pages of RetroArch.
After loading the core, I used the Load Content option to open Part 1 of Freedoom by selecting its .wad file that I downloaded earlier. As you can see in the video above, the game ran well. There were some minor stutters, but it didn’t affect gameplay; I was too busy taking down demons.
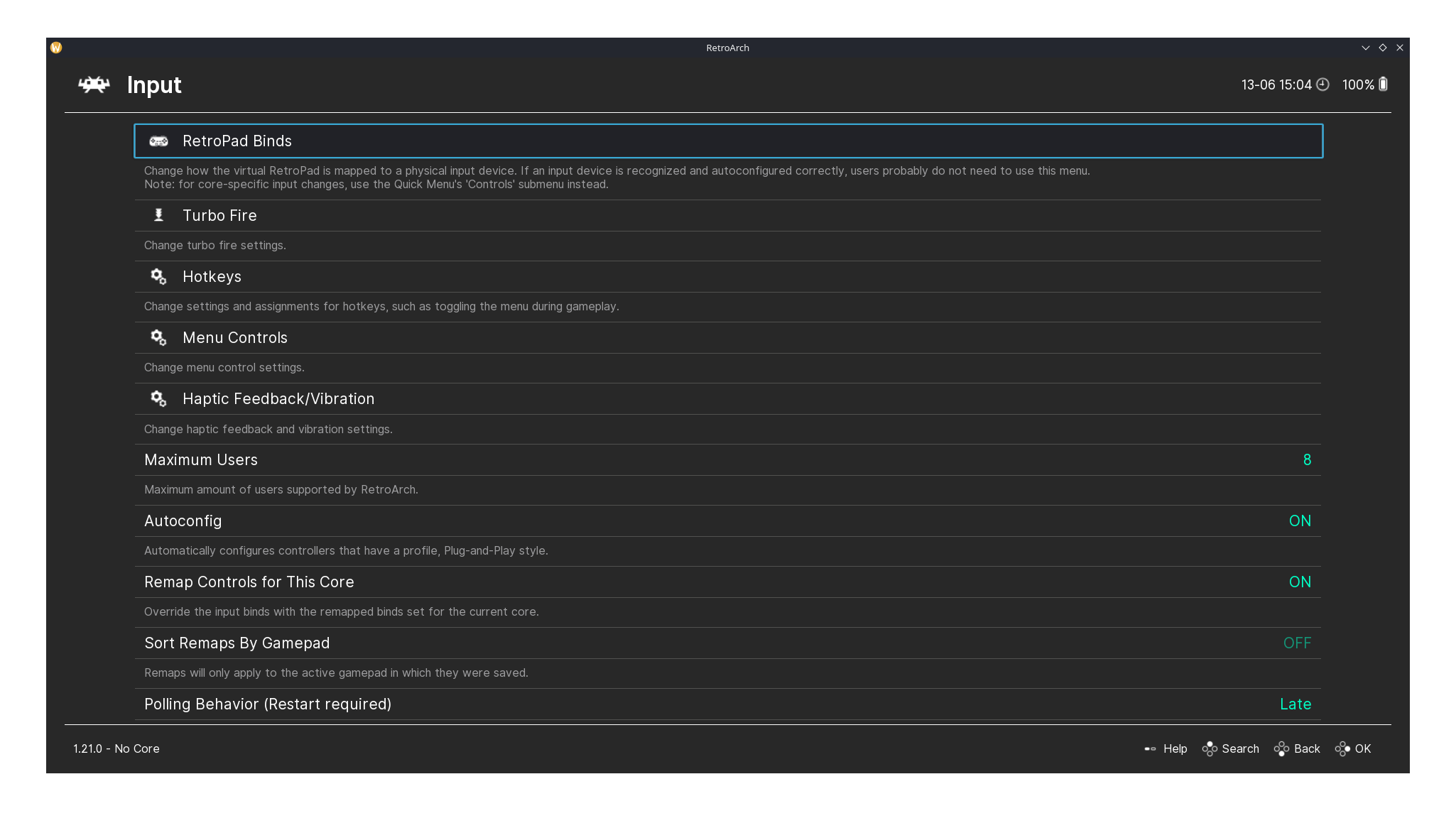
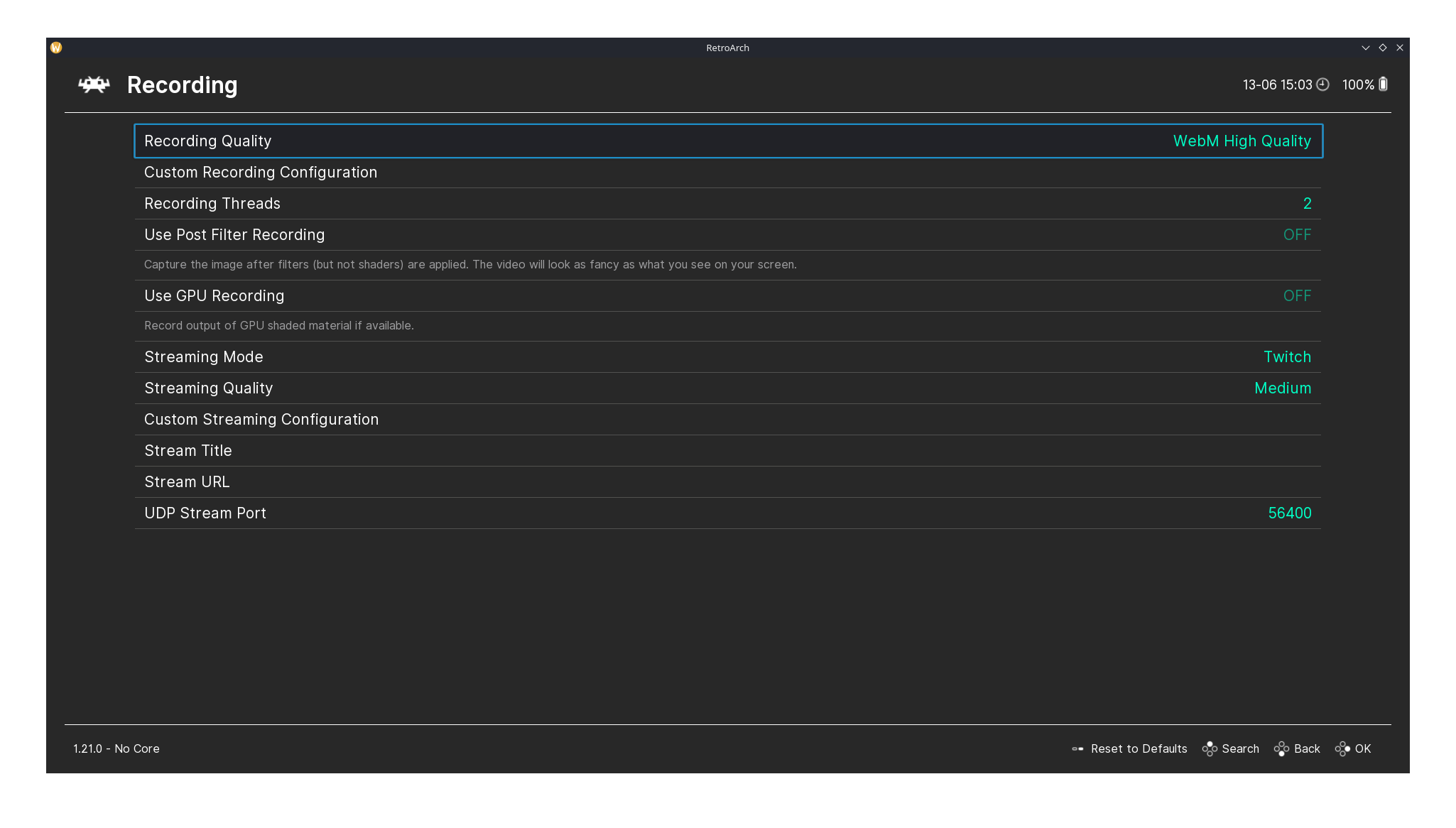
RetroArch's Input and Recording pages.
For those who like tinkering with their controller input, RetroArch’s Input page offers detailed customization, letting you remap buttons, adjust sensitivity, and set up different profiles for each core or game.
There’s also a Recording page where you can capture gameplay footage easily without needing extra software. (I missed this before I recorded the video.)
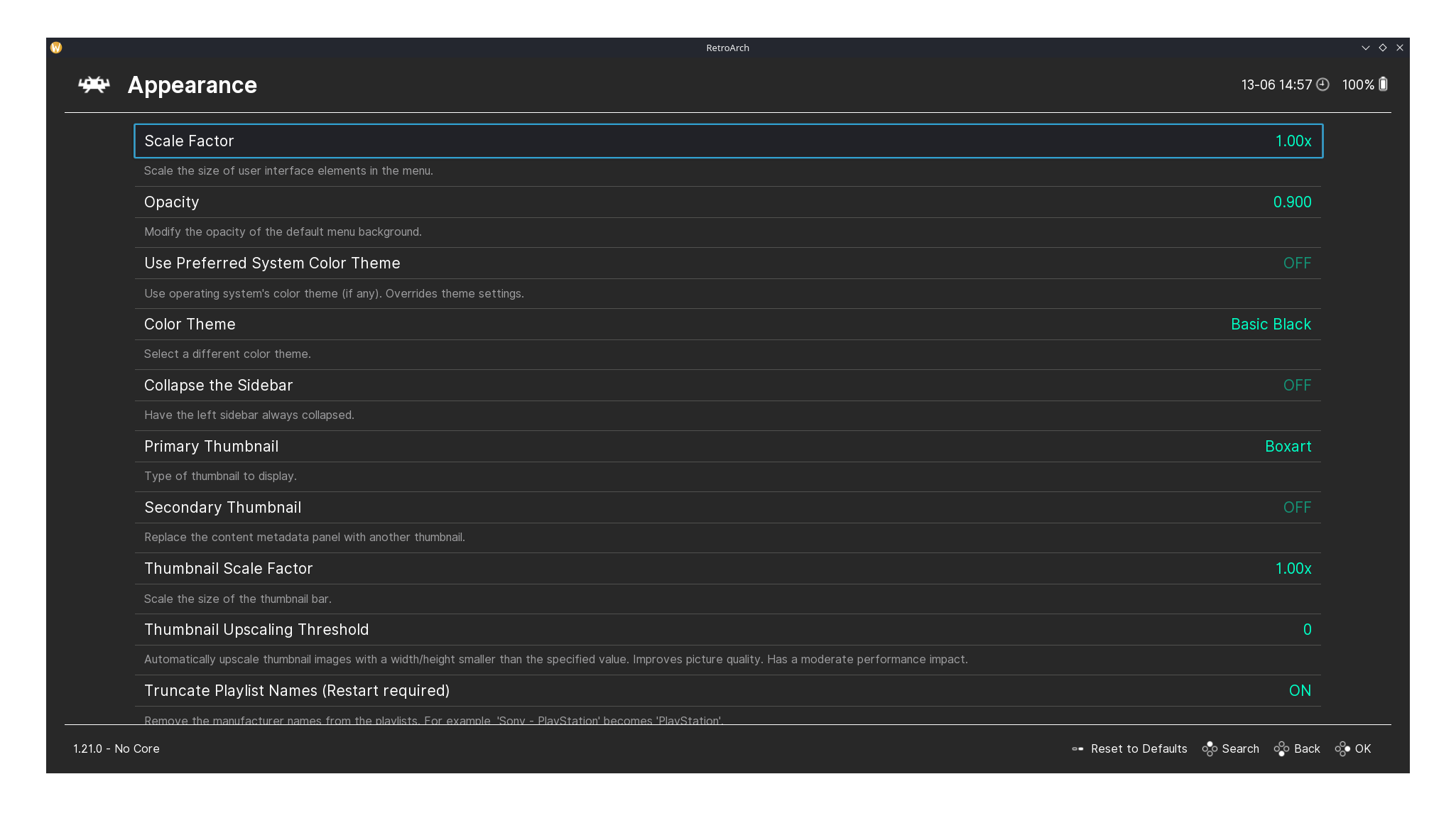
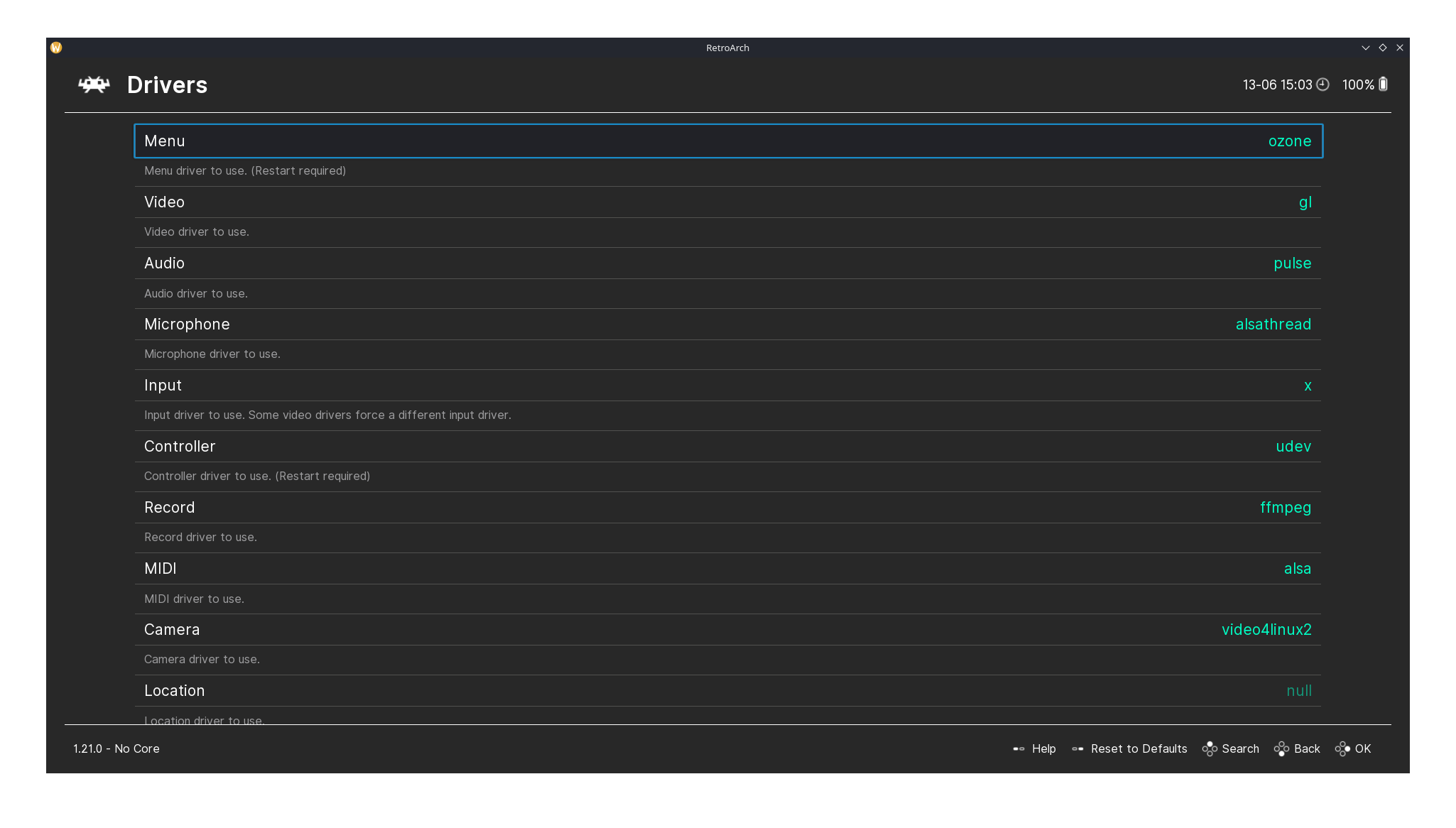
RetroArch's Appearance and Drivers pages.
Similarly, the Appearance page allows you to adjust themes, menu styles, and on-screen displays to suit your preferences, while the Drivers page lets you configure hardware settings like video, audio, input, and network interfaces to ensure smooth performance.
During my play session, RetroArch’s full-screen mode bugged out and wouldn’t enter full-screen properly, so I had to stick with windowed mode. There are other cool features I didn’t talk about, like Netplay for online multiplayer, Shaders to improve graphics, and Cheat Code support for games.
⚙️ Installing RetroArch on Linux
RetroArch comes in a bunch of formats, but on Linux, there are two main ways I recommend installing it. The first is to source it via Flathub by running the following command:
flatpak install flathub org.libretro.RetroArch
The second is for Ubuntu users who use snaps. You can grab the latest release from Snapcraft by running this command:
sudo snap install retroarch
You can also get RetroArch via Steam, AppImage, or build it from source. It’s cross-platform, with downloads available directly from the official website for other major systems like Raspberry Pi, Windows, Android, macOS, and iOS.
Suggested Read 📖
From It's FOSS News via this RSS feed






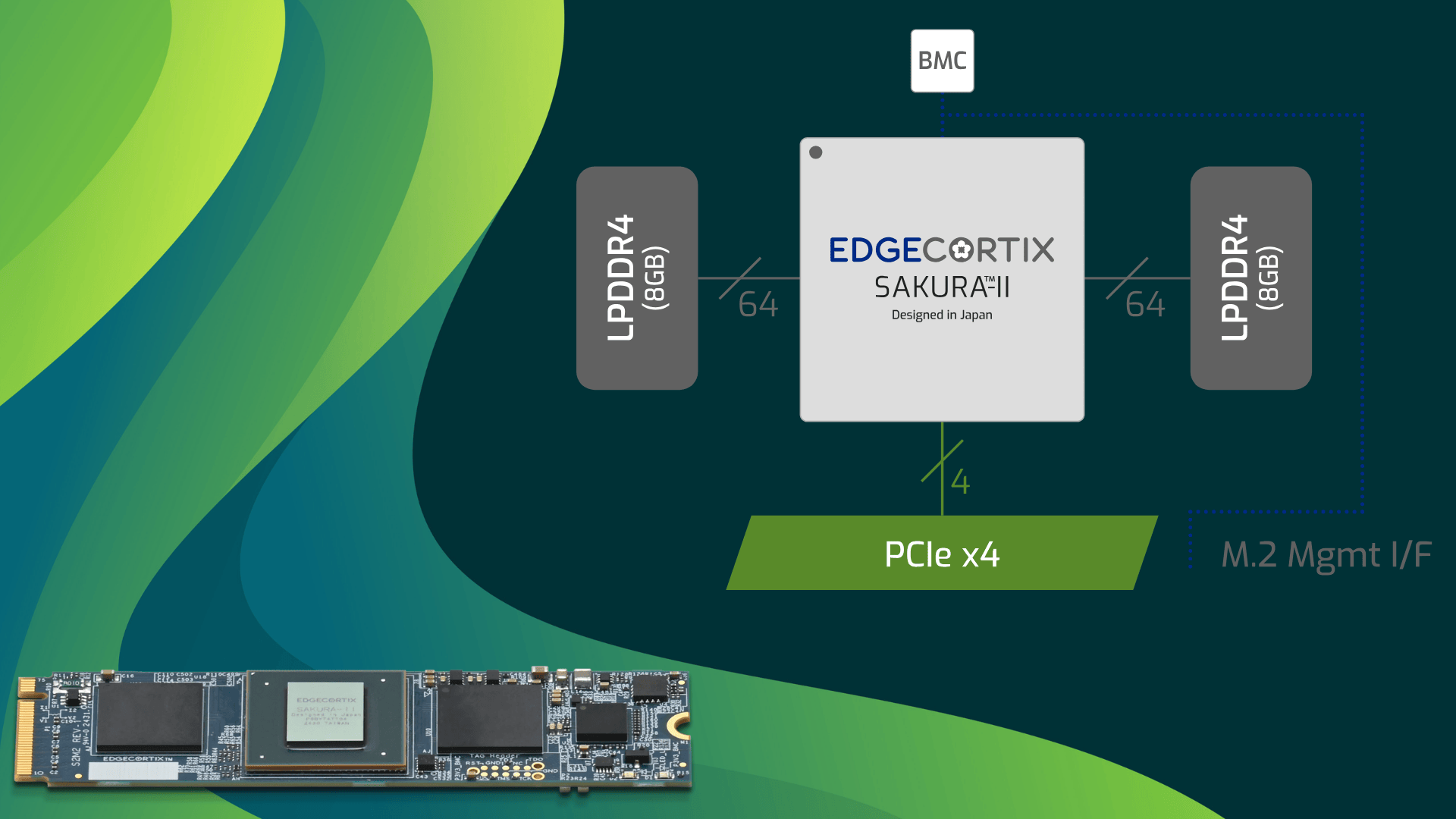 The SAKURA-II's
The SAKURA-II's 




 Source: Apple
Source: Apple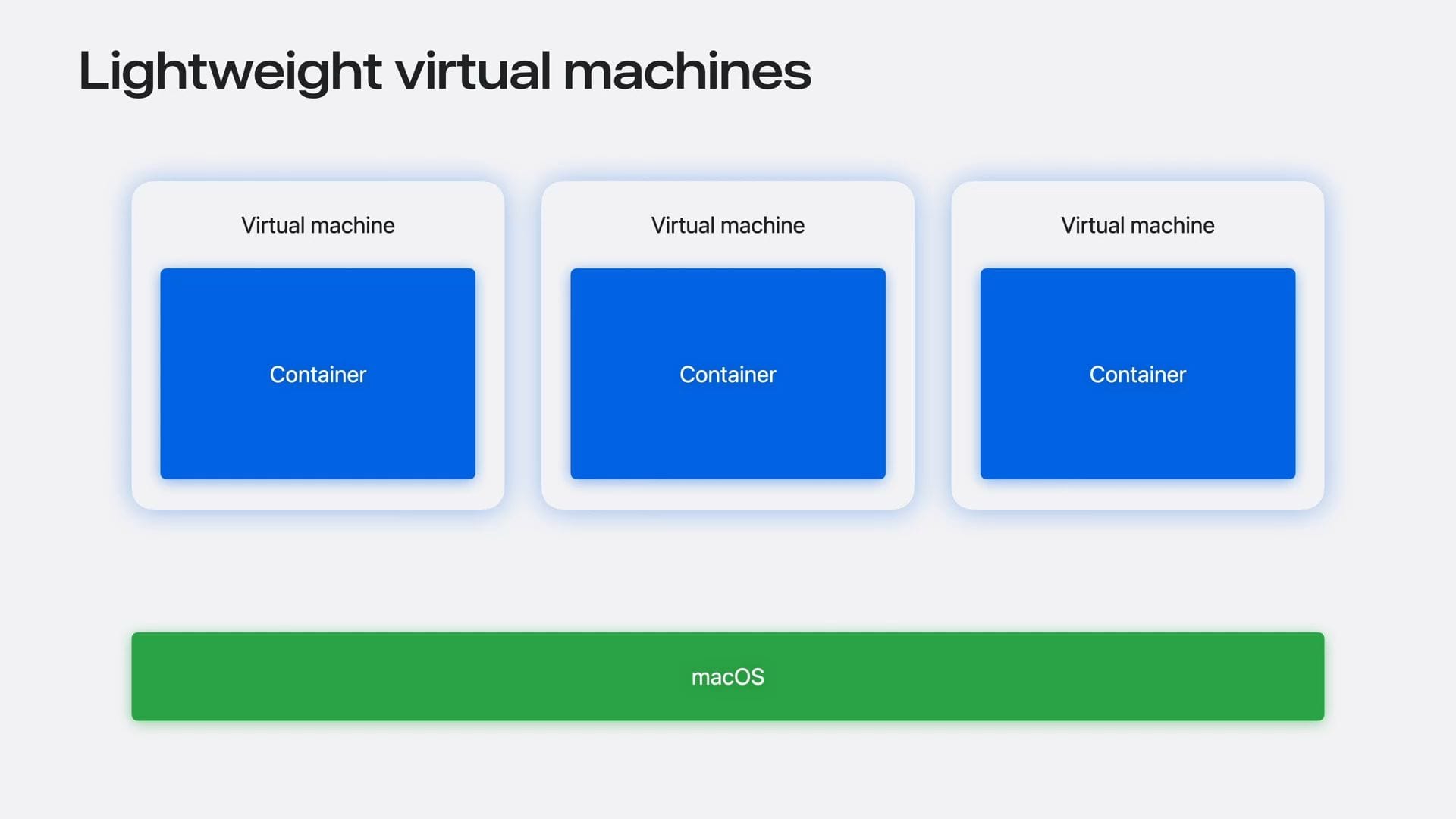 Source: Apple
Source: Apple
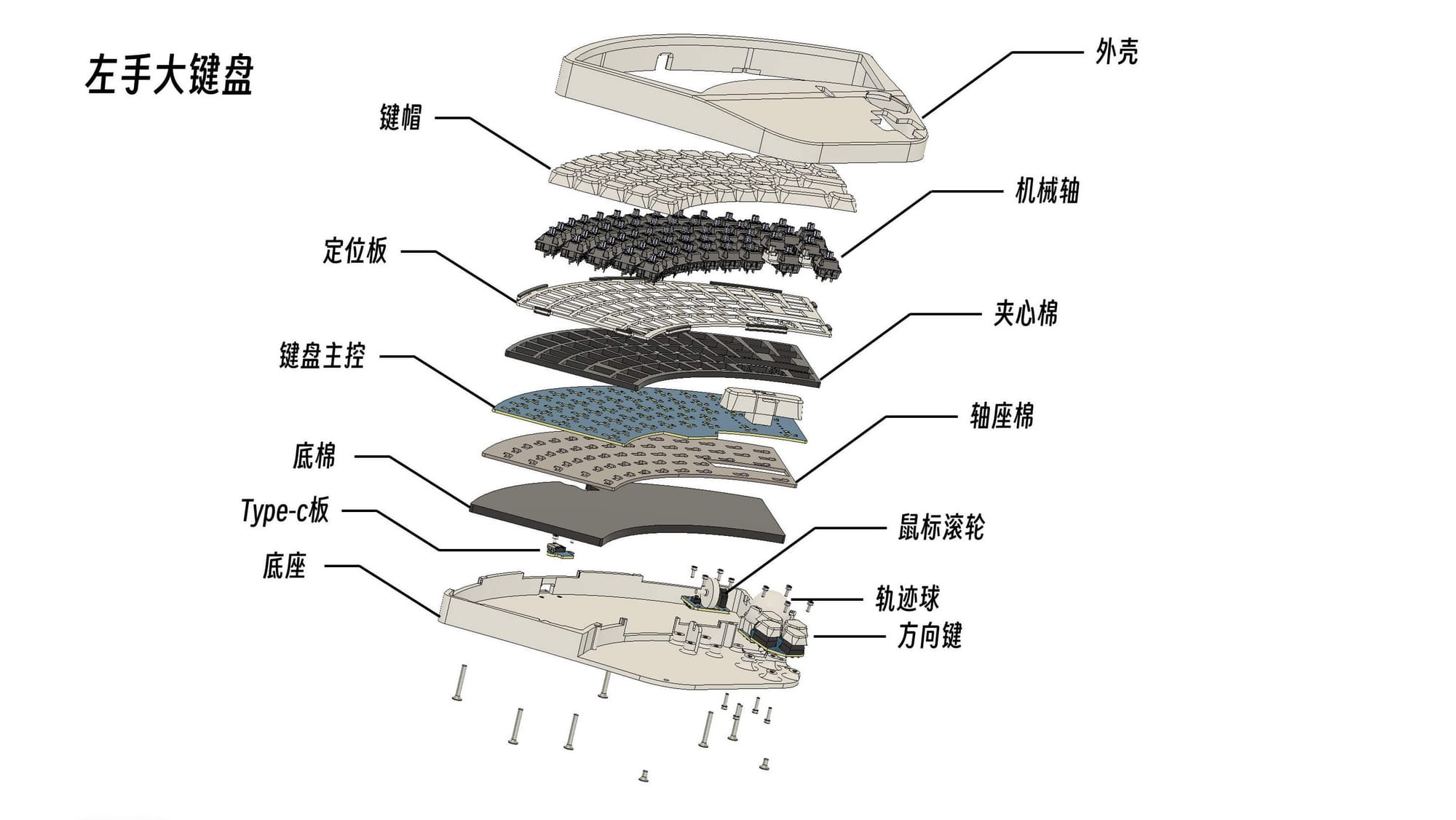 Source: HTX Studio
Source: HTX Studio





 Source:
Source: 


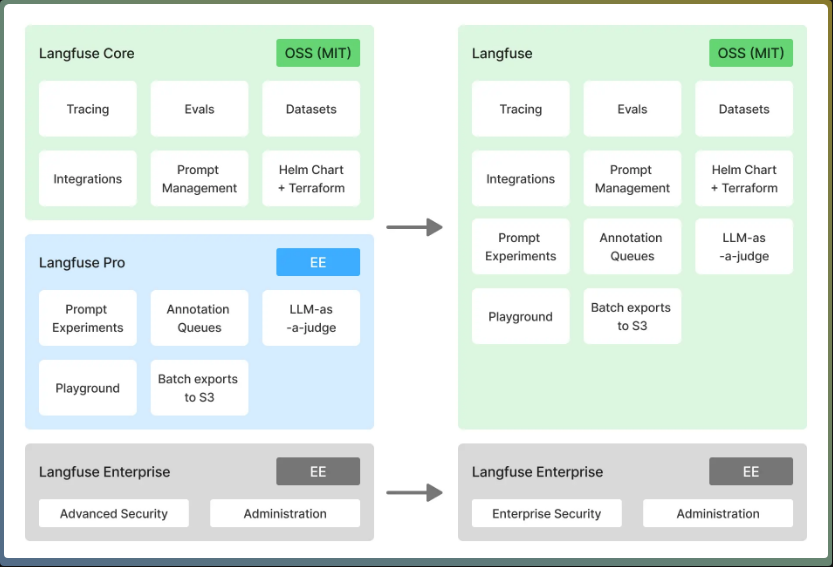 Source: Langfuse
Source: Langfuse
 Source: Elecrow
Source: Elecrow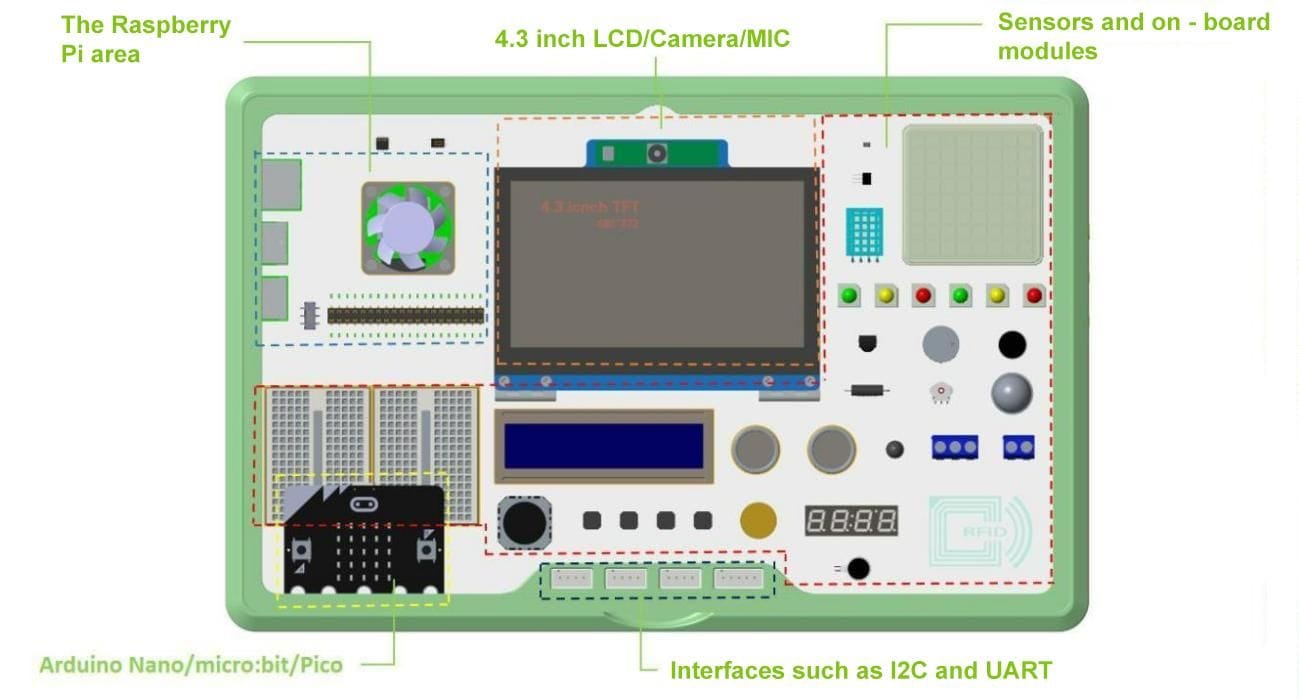
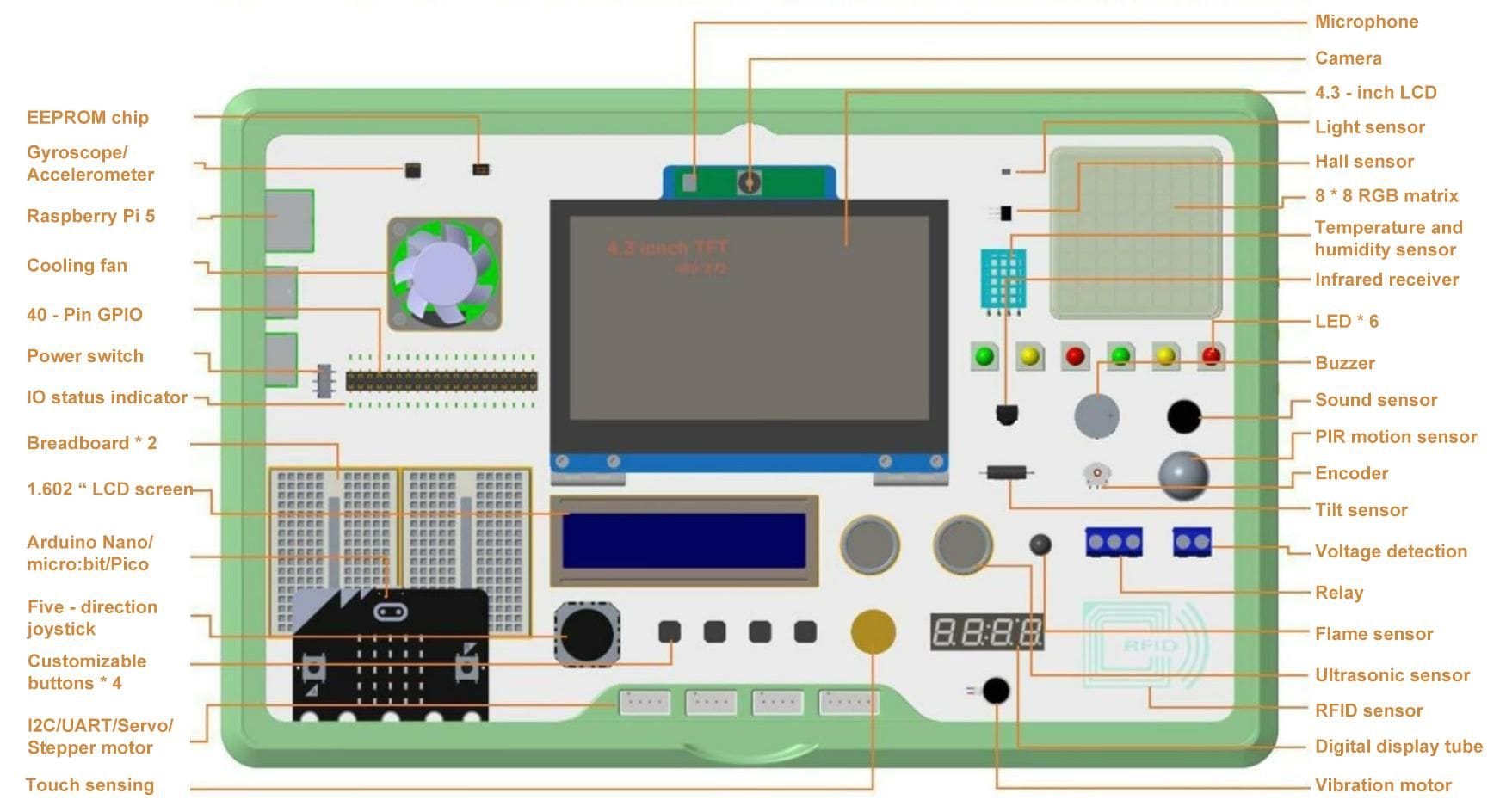

 Source: Jeff Geerling
Source: Jeff Geerling



 TPDE's GitHub repository.
TPDE's GitHub repository.



 The Tablet Mode looks nice.
The Tablet Mode looks nice.



 Snapshot 1 of Ubuntu 25.10.
Snapshot 1 of Ubuntu 25.10.

 Source: World Bank
Source: World Bank

 Source: FOSS Force
Source: FOSS Force